Difference between revisions of "DDDAS: Data Dynamic Simulation for Disaster Management"
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<tr style="page-break-inside: avoid; height: 12.15pt;"> | <tr style="page-break-inside: avoid; height: 12.15pt;"> | ||
<td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"> | <td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"> | ||
| − | <p><em>Ideas:</em>The goal of this project is to provide a data driven real-time atmosphere-wildfire model with data acquired from weather data streams, sensors on location, and airborne images. The project is developing new data driven assimilation methods for highly nonlinear problems. The model consists of an ensemble of simulation. The data assimilation methods modify the model from data that arrives while the model is running. | + | <p><em>Ideas:</em>The goal of this project is to provide a data driven real-time atmosphere-wildfire model with data acquired from weather data streams, sensors on location, and airborne images. The project is developing new data driven assimilation methods for highly nonlinear problems. The model consists of an ensemble of simulation. The data assimilation methods modify the model from data that arrives while the model is running.</p> |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr style="page-break-inside: avoid; height: 12.15pt;"> | <tr style="page-break-inside: avoid; height: 12.15pt;"> | ||
<td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"> | <td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"> | ||
| − | <p><em>Tools: | + | <p><em>Tools:</em>A data driven massively parallel software framework was developed to link data assimilation algorithms, data acquisition, and an ensemble of simulations.</p> |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
<td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"><br /></td> | <td colspan="2" style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 473.4pt; height: 12.15pt;" valign="top" width="789"><br /></td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
| − | |||
</table> | </table> | ||
| − | <table style="border-collapse:collapse;border:none;mso-border-alt:solid windowtext .5pt; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt;mso-border-insideh:.5pt solid windowtext; mso-border-insidev:.5pt solid windowtext" border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0" | + | <table style="border-collapse:collapse;border:none; mso-border-alt:solid windowtext .5pt; mso-padding-alt:0in 5.4pt 0in 5.4pt;mso-border-insideh:.5pt solid windowtext; mso-border-insidev:.5pt solid windowtext" border="1" cellpadding="0" cellspacing="0"> |
| − | |||
<tr style="mso-yfti-irow:0"> | <tr style="mso-yfti-irow:0"> | ||
<td style="border: 1pt solid windowtext; padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in;" valign="top" width="738"></td> | <td style="border: 1pt solid windowtext; padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in;" valign="top" width="738"></td> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 60: | ||
<tr style="height: 232.6pt;"> | <tr style="height: 232.6pt;"> | ||
<td style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in; height: 232.6pt;" valign="top" width="738"> | <td style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in; height: 232.6pt;" valign="top" width="738"> | ||
| − | + | [[File:Nuggett_fig02.jpg]]</td> | |
| − | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
<tr style="height: 98.5pt;"> | <tr style="height: 98.5pt;"> | ||
<td style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in; height: 98.5pt;" valign="top" width="738"> | <td style="padding: 0in 5.4pt; width: 6.15in; height: 98.5pt;" valign="top" width="738"> | ||
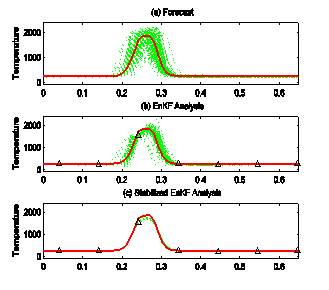
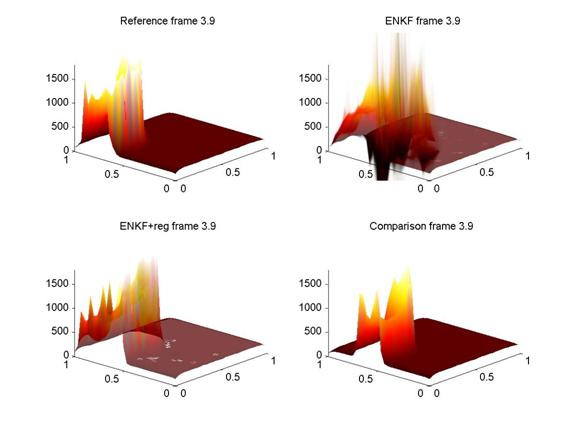
| − | <p><b>Description of Graphic Image:</b><br />Left to right and top to bottom: The <em style="mso-bidi-font-style:normal">Reference</em> solution represents the truth. Data assimilation by a standard <em>ENKF </em>algorithm results in an unstable solution because of the nonlinear behavior of wildfire. Stabilization gives the regularized solution <em>ENKF+reg</em>. Without data assimilation, the solution would develop as in the <em>Comparison</em>; the data assimilation shifts the model towards the truth. The model state is a probability distribution, visualized in the two ENKF figures as the superposition of transparent temperature profiles of ensemble members. | + | <p><b>Description of Graphic Image:</b><br />Left to right and top to bottom: The <em style="mso-bidi-font-style:normal">Reference</em> solution represents the truth. Data assimilation by a standard <em>ENKF </em>algorithm results in an unstable solution because of the nonlinear behavior of wildfire. Stabilization gives the regularized solution <em>ENKF+reg</em>. Without data assimilation, the solution would develop as in the <em>Comparison</em>; the data assimilation shifts the model towards the truth. The model state is a probability distribution, visualized in the two ENKF figures as the superposition of transparent temperature profiles of ensemble members.</p> |
</td> | </td> | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:26, 8 March 2010
|
Project Title: |
|
|
Investigators: Jan Mandel, Anatolii Puhalski, Craig Johns, Leopoldo P. Franca, Craig C. Douglas, Janice L. Coen, Anthony Vodacek, Robert Kremens, Guan Qin |
|
|
Institution: |
|
|
Website: |
Description of Graphic Image: |
|
Project Description and Outcome |
|
|
Ideas:The goal of this project is to provide a data driven real-time atmosphere-wildfire model with data acquired from weather data streams, sensors on location, and airborne images. The project is developing new data driven assimilation methods for highly nonlinear problems. The model consists of an ensemble of simulation. The data assimilation methods modify the model from data that arrives while the model is running. |
|
|
Tools:A data driven massively parallel software framework was developed to link data assimilation algorithms, data acquisition, and an ensemble of simulations. |
|